The introduction of innovation in education aims to be implemented through specific non-formal educational programmes, tailored to different age groups, to support and deepen the understanding of cutting-edge issues and promote the integration of new teaching and learning practices on the basis of creativity and inquiry based learning as well as of interaction with experts outside the classroom.
These educational programmes aim to prepare students for integration into the 21st century society through a holistic approach to knowledge, the cultivation of digital skills, mental skills, creative skills and the promotion and reinforcement of positive attitudes towards knowledge.
All educational programmes, scenarios and teaching materials under development are foreseen to be accompanied by manuals and escorting material for students and teachers.
The developement of the Innovation Centres is expected to contribute to the further development of students' skills by encouraging and motivating them to engage and deepen as well as to pursue future studies and careers in STEM, thereby improving the country's human resources and its competitiveness in the field of science and technological development.
At the same time, the project aims to align with the UN Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) and the updated EU Digital Education Action Plan (2021-2027). 
Priorities of the updated "Action Plan for Digital Education (2021-2027)" (ECA, 2023)
Pedagogical/teaching approaches
The OECD reports (2018, 2020) explore new forms of teaching, learning and assessment ("Innovative Pedagogies for Powerful Learning" (IPPL)) for an interactive world that will support educators and policy makers in producing innovative practices in education (Kukulska-Hulme et al, 2020).
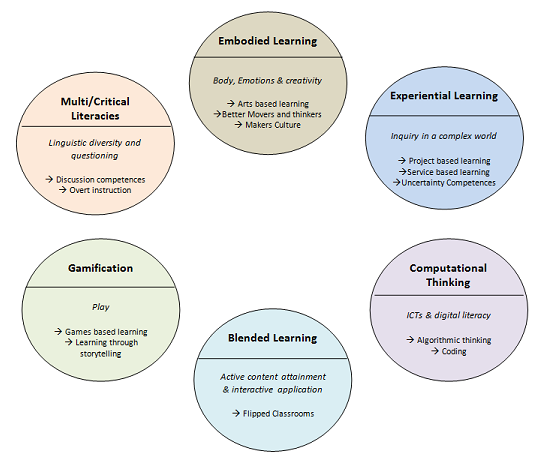
Innovative Pedagogies for Powerful Learning (OECD, 2017)
Innovative pedagogical and teaching approaches that the project will exploit:
- AI in Education - Preparing for life and learning in the AI era.
- Meta-humanistic perspectives - Addressing the relationship between humans and technology.
- Learning from open information sources - Using real world data for personal learning.
- Inclusion of data ethics - Ethical use of data in digital life and learning.
- Social justice pedagogy - Addressing injustices in life and society.
- e-sports - Learning and teaching through competitive virtual play.
- Learning through animation - Watching and interacting with short animations.
- Multisensory Learning - Using multiple senses to enhance learning.
- Offline learning - Online learning over the Internet.
- Online workshops - Workshops for all.